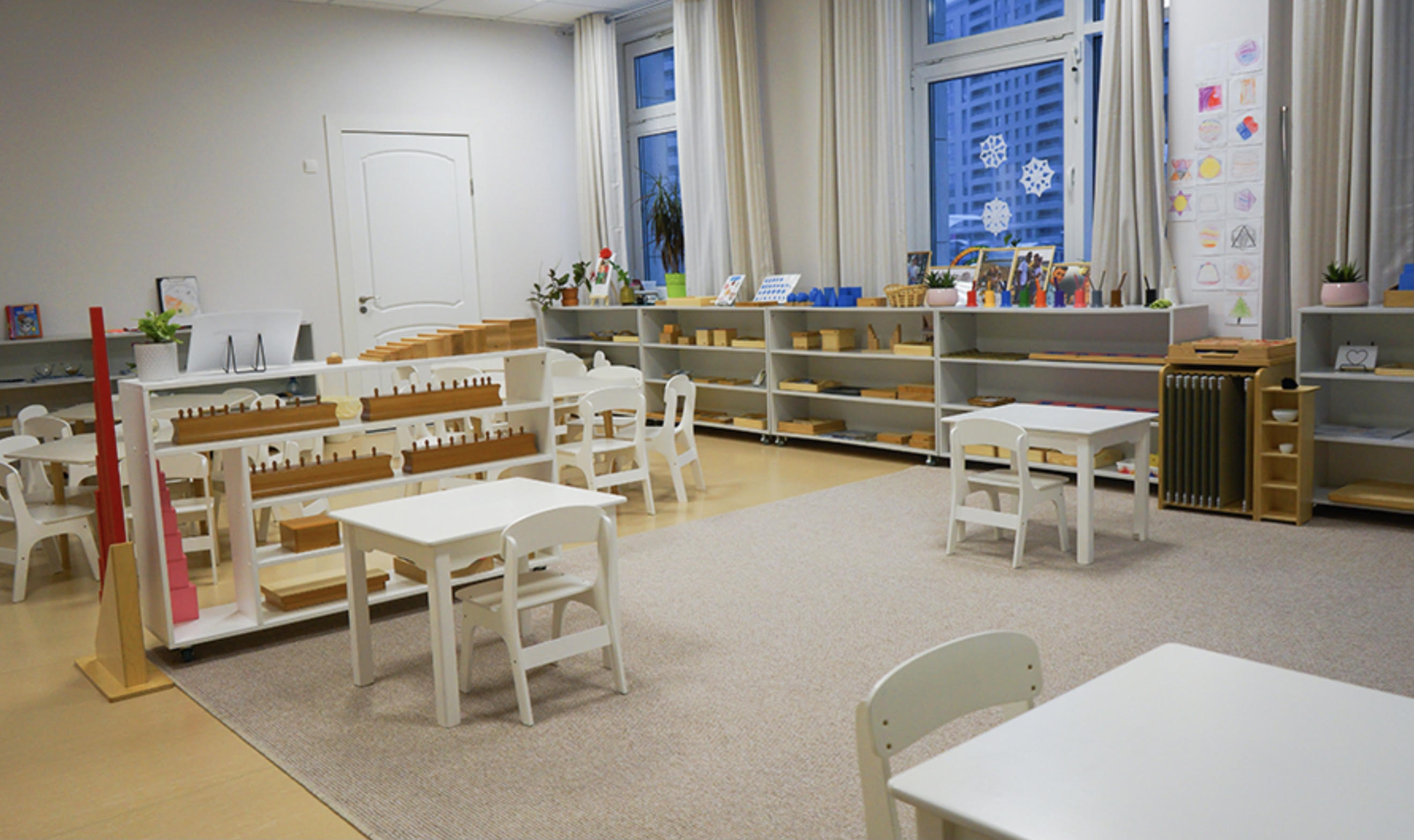
Montessori education is an educational approach developed by Italian physician and educator Maria Montessori (1870-1952).

Montessori education is practiced in an estimated 20,000 schools worldwide, serving children from birth to eighteen years old.
Montessori education is characterized by an emphasis on independence, freedom within limits, and respect for a child’s natural psycholo gical development, as well as technological advancements in society.
gical development, as well as technological advancements in society.
Although a range of practices exists under the name "Montessori", the Association Montessori Internationale (AMI) and the American Montessori Society (AMS) cite these elements as essential:
Mixed age classrooms, with classrooms for children aged 2½ or 3 to 6 years old by far the most common.
Student choice of activity from within a prescribed range of options.
Uninterrupted blocks of work time.
A Constructivism or "discovery" model, where students learn concepts from working with materials, rather than by direct instruction.
Specialized educational materials (Montessori Materials) developed by Maria Montessori and her collaborators.

In addition, many Montessori schools design their programs with reference to Montessori’s model of human development from her published works, and use pedagogy, lessons, and Montessori Materials introduced in teacher training derived from courses presented by Maria Montessori during her lifetime.
















